Retinal degenerative diseases, such as age-related macular degeneration (AMD) and retinitis pigmentosa (RP), affect approximately 200 million and 1.5 million people worldwide, respectively. These conditions lead to the progressive loss of retinal cells, ultimately resulting in irreversible vision impairment. Currently, no effective therapeutic solution exists for the majority of patients.
Regenerative medicine, which aims to replace damaged retinal cells with laboratory-grown cells, represents a promising avenue of research. It is within this context that the eRETINA project was launched, stemming from a collaboration initiated in 2016 between the Center for the Study of Stem Cells (CESC/I-Stem) and the Center for Nanoscience and Nanotechnology (C2N) at the Université Paris-Saclay.
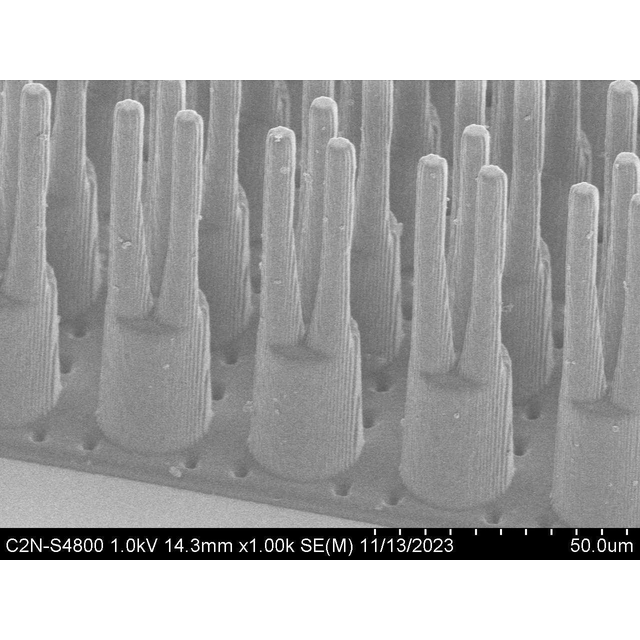
The goal of eRETINA is to develop a next-generation retinal tissue using bioengineering techniques. These implantable tissues are composed of flexible, biocompatible polymer membranes with microstructured surfaces, forming a three-dimensional (scaffold) structure developed in C2N’s technology facility.
In parallel, biocompatibility tests have been conducted in the cell culture laboratory (L2) of C2N’s Biotech platform using retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) cells. These scaffolds are designed to host and promote the maturation of specific retinal cells, particularly photoreceptors (PRs) and RPE cells, which are derived from pluripotent stem cells at CESC/I-Stem.
The first in vivo studies of these implants are scheduled to take place between late 2024 and early 2025 at CESC/I-Stem.
Project eRETINA Contacts at C2N:
Dr. Frédéric Hamouda (Research Engineer) frederic.hamouda@c2n.upsaclay.fr, Center for Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, Université Paris-Saclay.
Patent and Communications 2019-2023
Patent No. 21 07934 (Publication No. 3 125 538) 22/07/21.
N. Perrin, et al. ‘’Biocompatible supporting retinal pigment epithelial, cell growth as part of a solution against retinal degeneration’’, FSSCR 2024, 22-24th January, Paris.
C. Geiger, et al.,’’Development of a micro-structured scaffold by 3D lithography for retinal tissue bioengineering”, FSSCR 2024, 22-24th January, Paris.
F. Hamouda, et al.,” Micro-structured scaffold membranes for retinal tissue bioengineering by two-photon lithography”, 48th International Conference on Micro and Nano Engineering, Leuven, Belgium, 19-23 september 2022.
C. Geiger, et al.,“Development of a micro-structured scaffold by 3D lithography for retinal tissue bioengineering”, FSSCR 2021, Montpellier, Nov 9-10.
E. Herardot, et al., “Retinal tissue bio-engineering from human pluripotent stem cells as a substitutive strategy for retinal degenerative disease”, 6th World Congress of the Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine International Society (TERMIS 2021), 15 - 19 November 2021 in the MECC in Maastricht, The Netherlands.
E. Herardot, et al., “Retinal tissue bio-engineering from human pluripotent stem cells as a substitutive strategy for retinal degenerative disease”,3rd meeting FSSCR, novembre 2019.
F. Hamouda, et al., “3D Scaffolds by soft lithography for retinal tissue reconstruction”, 45th International Conference on Micro and Nano Engineering, Rhodes, Greece, 23-26/09/2019.
Figure : SEM observation of the microstructured membrane (25mm²) dedicated to photoreceptors (PRs), fabricated in the Nanotechnology Facility at C2N.