Two researchers of the Centre de Nanosciences et de Nanotechnologies – C2N (CNRS/Université Paris-Sud), have recently published an article in the journal Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics (PCCP) about plasmon lasers.
Plasmon lasers are a new class of coherent light sources that use metals for light localization and amplification. Access to this confined light that couples to the oscillating electrons of metal enables reducing the physical size and mode volume of the laser much below the diffraction limit. The race to demonstrate new plasmon nanolasers has enabled considerable progress over the last several years regarding nanocavity design, operating temperature, pumping conditions, and material efficiency of both plasmonic nanocavity and gain medium.
This article discusses some of the latest developments of coherent nanoscopic light sources, in metallic and dielectric lasers, with a specific focus on plasmon nanolasers. The researchers highlight recent advances in plasmon lasers through plasmonic nanoparticle arrays: beam directionality, wavelength tunability, multi-modal emission, and dark and bright modes lasing. They also discuss future prospects.
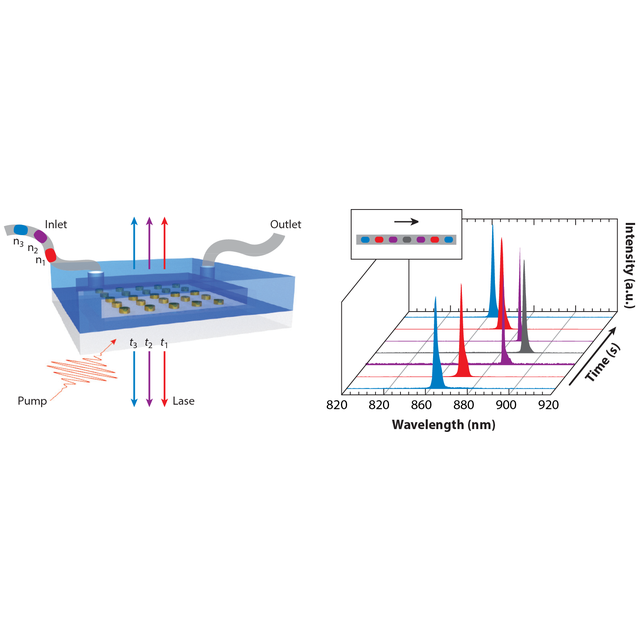
Figure : Tunable plasmon laser based on nanoparticle arrays. Scheme of the real-time tunable laser and lasing emissions shifting to longer wavelengths and then back to shorter wavelengths. © C2N / C. Deeb- Reference:
Plasmon lasers: coherent nanoscopic light sources
Claire Deeb and Jean-Luc Pelouard
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2017, 19, 29731
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1039/c7cp06780a
- Contact: Claire Deeb